
As Business Owners are you confronted frequently with Supply Chain issues such as:
- Weak demand forecasting
- Lack of supply chain visibility
- Tedious manual processes
- Escalating supply chain costs
- Missing communication among stakeholders
You are not alone.
Yes, just not alone!
Frontiers of world markets ae expanding thick and fast.
Business competition is mounting by the day.
Managing the entire process of demand and supply in synchronized fashion is order of the day.
Any failure in this direction can turn out to be disastrous to the business.
To salvage the situation full attention to Supply Chain Management Is badly warranted.
Meaning of Supply Chains
Supply Chains involve the processes that create system which makes people, resources, information and organizations to work together to move products and services from suppliers to consumers.
Connotation of Supply Chain Management
Supply Chain Management is a systematic and strategic management of the product from raw material to finished goods.
Supply Chain Management (SCM) involves the design, control and monitoring of Supply Chain activities.
The underlying objective is:
- Creating net value.
- Building a competitive infrastructure.
- Leveraging logistics.
- Synchronization of demand and supply.
- Measurement of performance.
Immediately after accomplishing the marketing task, it is incumbent upon the company to offer the product:
- At a place where the consumer wants it.
- At a time that he wants it.
- Ansure its physical distribution.
This is the essence of Supply Chain Management.
7 R’s Of SCM
SCM entails 7 R’s in the entire management process.

Objectives of Supply Chain Management

- Maximization of Value Generation
The Supply chain Profitability in SCM stands for the difference between the amount paid by the customer to purchase a product and the cost incurred by an organization to produce and supply the product to the customer.
- Cost Quality Optimization
SCM seeks to achieve cost quality balance and optimization.
- To look for sources of Cost and Revenue
Since customer is the only source of revenue, it is essential to have. An appropriate management of the flow of information, product or funds.
- Shortening Ordering Time
SCM aims to reduce the time required for ordering and its fulfilment.
- Delivery optimization
The SCM aims to meet the demands of the customer for guaranteed delivery of high quality and low cost with less lead time.
- Demand fulfilment
Managing the demand and supply to fulfil customer demand through efficient resources.
- Flexibility
A Well managed supply chain provides flexible planning and better control mechanism.
- Better Distribution
The marketer can achieve optimized level distribution by using all resources that are available properly.
- Cost Reduction
SCM reduces companies operating expenses, business expensives by establishing an optimised supply chain. It shortens the holding period for both raw materials and finished goods. These measures help in reducing losses and keep the cost of doing the business as low as possible.
SCM aims to reduce the system wise cost of a company to meet service level requirement.
Other auxiliary sub-objectives derived from long term objectives are:
- Inventory reduction with the value chain.
- Reduction of warehousing costs.
- Acceleration of cash to cash cycle.
- Reduction in throughput times.
- Improvement in delivery reliability.
Nature of Supply Chain Management
Supervise Production Process
Supply chain management supervises the whole production processes of business for deriving optimum results with minimum wastage.
Timely Delivery of Goods
SCM ensures timely delivery of goods and services by bringing proper coordination in between distinct transportation channels and warehouses.
Proper Return System
SCM facilitates an effective return mechanism through an automated process on both buy and sell-side of the business. All refunds and claims of customers, distributors and suppliers are settled instantly via this process. Super chain management ensures proper handling and inspection of defective goods.
SCOPE of Supply Chain Management
Supply Chain Management enjoys very vast scope encompassing multiple business functionalities:
- Planning, design, control and implementation of all business processes related to procurement, manufacturing, distribution and sales order fulfilment.
- Managing supply and demand.
- Sourcing raw materials and parts.
- Manufacturing and assembly.
- Warehousing and inventory tracking.
- Order entry and order management.
- Distribution across all channels.
- Delivery to the customer.
Supply chain management is the integration of businesses from end user through original suppliers.
Networks of suppliers and service providers have to be integrated and coordinated to ensure that the raw material moves smoothly from various procurement points to the centers of production.
Moreover, the finished goods move smoothly from the centers of production to the various points of sale/ delivery to consumer across the globe
5 Components of Supply Chain Management
1. Planning
Plan and manage all resources required to meet customer demand for a company’s product or service. When the supply chain is established, determine metrics to measure whether the supply chain is efficient, effective, delivers value to customers and meets company goals.
2. Sourcing
Choose suppliers to provide the goods and services needed to create the product. Then, establish processes to monitor and manage supplier relationships. Key processes include – ordering, receiving, managing inventory and authorizing supplier payments.
3. Manufacturing
Organize the activities required to accept raw materials, manufacture the product, test for quality, package for shipping and schedule for delivery.
4. Delivery and Logistics
Coordinate customer orders, schedule deliveries, dispatch loads, invoice customers and receive payments.
5. Return
Create a network or process to take back defective, excess or unwanted products.
Basic Premises of Supply Chain Management
1. Demand planning and forecasting.
2. Demand collaboration, i.e., collaborative resolution process to determine consensus forecasts.
3. Order promising, i.e., when can one promise a product to a customer taking account lead times and constraints.
4. Strategic network optimization, i.e., what plants and distribution channels should serve, what markets for what products whether monthly — yearly.
5. Production and distribution planning, i.e., coordinate the actual production and distribution plans for a whole enterprise may be on a daily basis.
6. Production scheduling.
7. Plan of reduction of costs and management of the performance, i.e., diagnosis of the potential and the indicators, the organization, evaluation and accounting reporting, evaluation and reporting quality.
SCM works on the Five Basic Components:
Plan – Source – Make – Deliver – Return
The efficient functioning of the supply chain involves:
1. Customer Service Standardization
2. Transportation
3. Inventory Management
4. Warehousing
5. Purchase
6. Information Maintenance
Functions of Supply Chain Management

- Purchasing
It is essential that the materials are procured and delivered on time during the manufacturing process. Here, coordination with suppliers and delivery companies is essential to avoid delays.
- Operations
Forecasting and demand planning is needed before materials are procured. Enterprises accurately forecast demand to avoid having too little or too much inventory that would lead to revenue losses.
It is essential that forecasting and demand planning are tied in with inventory management, production and shipping.
- Logistics
Logistics co-ordinates all planning aspects, purchasing, production, and transportation aspects to ensure that products reach the end consumer without hindrances.
It is essential to have co-ordination with multiple departments. Quick shipment to customers warrant better co-ordination.
- Resource Management
Resource management entails right resources allocation to the right activities for optimization. It ensures that optimized production schedule is created to maximize operations efficiency.
- Information workflow
A consistent system of information workflow is necessary to ensure that everyone is working on the same set of data. This will check miss communications and avoid any waste of time.
Role of Supply Chain Management
Doubtless to say that Supply Chain Management is.. the back-bone of a business.
An effective supply chain management that will ensure an effective Market Coverage and the availability of the right product at the right places across various locations in the country.
Inventory control and visibility have a direct impact on the cost of production and hence a direct impact on the profitability of the organization.
The lesser the capital locked up in inventory the more will be the profitability and vice versa.
Today inventory or stock of finished goods is held at many distribution centers.
“Every company needs thinking globally about business, and strategically about technology”
(MR. Supply Chain )
- Boosts Customer Service
Customers expect the right product to be delivered at the right location. They expect right delivery time and also right after sale support. Customers expect products to be serviced quickly. Therefore considering all of this, the significance of SCM is critically high.
- Reduces Operating Costs
Retailers depend on supply chains to deliver expensive products in order to avoid holding costly inventories in stores any longer than it is required. Manufacturers rely on supply chain to deliver reliably to avoid material shortages.
- Improves Financial Position
Supply chain management helps in controlling and reducing supply chain costs. It not only saves costs but also dramatically increases firm’s profits.
- Momentum
SCM streamlines everything, from product flow to any unexpected natural disasters. With effective SCM, organizations can diagnose any sort of problem easily.
- Integrated and Co-operative Logistics
Effective supply chain meets the requirements of producers and consumers. It takes an integrated approach towards management.
Role of Logistics
Logistics is the back bone of the supply chains. Logistics refers to the management of flow of goods and supplies involving information, data and documentation between two entities or points.
Logistics plays an important role in the post procurement function of delivery of raw material and supplies from the supplier to the factory or production center and the dispatch of finished goods from the factory to the point of delivery to the customer.
5 Fundamental Features of Supply Chain Management
1. Single Entity
For a variety of planning and control functions across the supply chain, the responsibility will lie with single entity.,
A group consisting of representatives from purchase, manufacturing, distribution and sales could be the entity for finalizing:
- Procurement plan
- Marketing plan
- Dispatch plan
- Production plan
This will reduce administrative delays and improve empathy across the supply chain
2. Inventory Perspective
The key measures that would facilitate inventory in supply chain management are:
- Improving flexibility
- Reducing lead times
- Reducing uncertainties
- Improving quality
3. Strategic Decision-Making:
The decisions in the supply chain are viewed for strategic implications rather than just operational..
4. Systems Approach:
The supply chain from vendor to customer is considered as a single integrated system rather than as many subsystems interfacing with each other.
5. Doing to the Best of Ability
It is important to focus on what one can do best. This has implications on outsourcing or even insourcing and building effective partnerships.
5 Cs of Supply Chain Management
IDC’s Simon Ellis ¹ defines what supply chain management is by identifying the five “Cs” of the effective supply chain management of the future:
• Connected
Being able to access unstructured data from:
- Social media,
- Structured data from the Internet of Things and
- More traditional data sets available through traditional ERP and B2B integration tools.
• Collaborative
Improving collaboration with suppliers increasingly means the use of cloud-based commerce networks to enable multi-enterprise collaboration and engagement.
• Cyber-aware
The supply chain must harden its systems and protect them from cyber-intrusions and hacks, which should be an enterprise-wide concern.
• Cognitively Enabled
The AI platform becomes the modern supply chain’s control tower by collating, coordinating and conducting decisions and actions across the chain. Most of the supply chain is automated and self-learning.
• Comprehensive:
Insights will be comprehensive and fast.
“The real competition is between supply chains, not companies”
(Martin Christographer)
4 Notable Pre-requisites of Supply Chain Management
(i) Efficiency:
The principle of efficiency requires that any supply chain should be conscious of cost reduction in all the activities and programs.
Efficiency leads to reduction in the wastage of resources, including wastage of time.
The principle of efficiency is reflected in initiatives such as just-in-time (JIT) inventory management.
The principle of efficiency also drives firms to achieve better planning and coordination of activities.
(ii) Reliability
Reliability is associated with consistency.
To a customer, the supply chain should ensure consistency of service. Consistency should be measured mainly in terms of the consistent delivery time achievement, accuracy in order fulfilment, consistency and accuracy in payment processing time, installation support, and after-sales service.
To achieve consistency, the processes have to be perfectly synchronized to the maximum extent possible across every link in the supply chain.
Reliability is very important since the globalized nature of supply chain relationships and criticality of the network linkages lead to a high level of dependency.
Disruption in the availability of even some small components could bring an entire assembly line to a complete halt, leading to huge losses across the entire supply chain.
(iii) Flexibility
Flexibility is also termed as the ‘agility’ of the supply chain. Flexibility involves capabilities such as:
- Ramping up production at the minimum of time intervals if required.
- Responding to changing patterns of demand.
- Customized transactional processes, as well as streamlined and rapid data flow.
(iv) Innovation
Innovation could generate a sustainable competitive advantage for the firm.
Supply chains that do not innovate will slowly erode their comparative advantage with regard to their competitors.
7 Golden Principles of Supply Chain Management
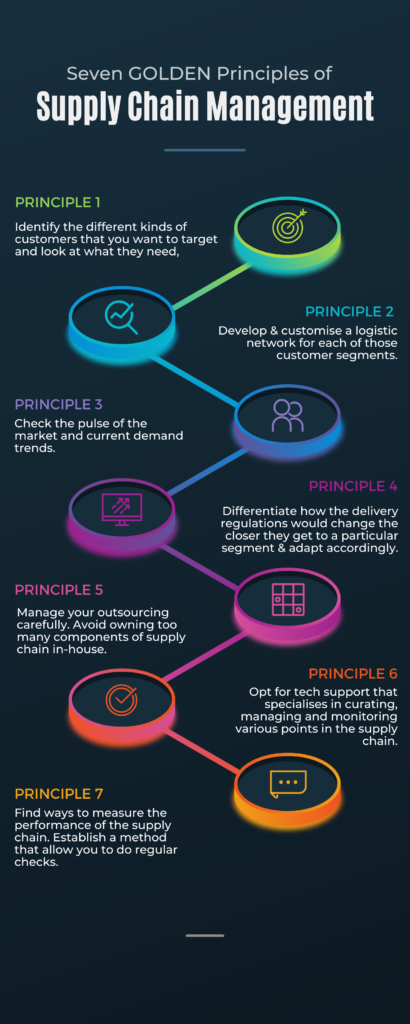
Successful execution of Supply Chain Management warrants compliance with 7 Golden
Principles
7 Golden Rules to be born in mind for successful execution of Supply Chain Management are:
- Identify target customers to ascertain their needs and adapt supply chain accordingly.
- Develop and customize logistic network to cater to specific need of customer segments.
- Identify the market demand pattern to align it to supply chain.
- Differentiate delivery regulations according to the requirements of customers segments.
- Retaining only core components to yourself and outsource the rest.
- Adopt tech support for curating, managing, monitoring various points of supply chain.
- Establish regular analytics method to measure performance of supply chain.
In Retrospect
Supply Chain transformation is primarily governed by profit motivation of business.
Gartner recommends flexibility and resilience for sustainable profit.
Sustainable Profit consists of:
Resilient Profit
“Supply chains must cope with the rising rate of disruption the world experiences”
Durable Profit
‘Supply chains must adapt to new realities to deliver profit in the long term.’
Holistic Profit
‘Supply chains must account for externalities that are the result of these activities”
‘Supply chain is the science. Logistics is the art”
(RDML Fabry)



